Active Transport-Types, Examples, and Mechanism
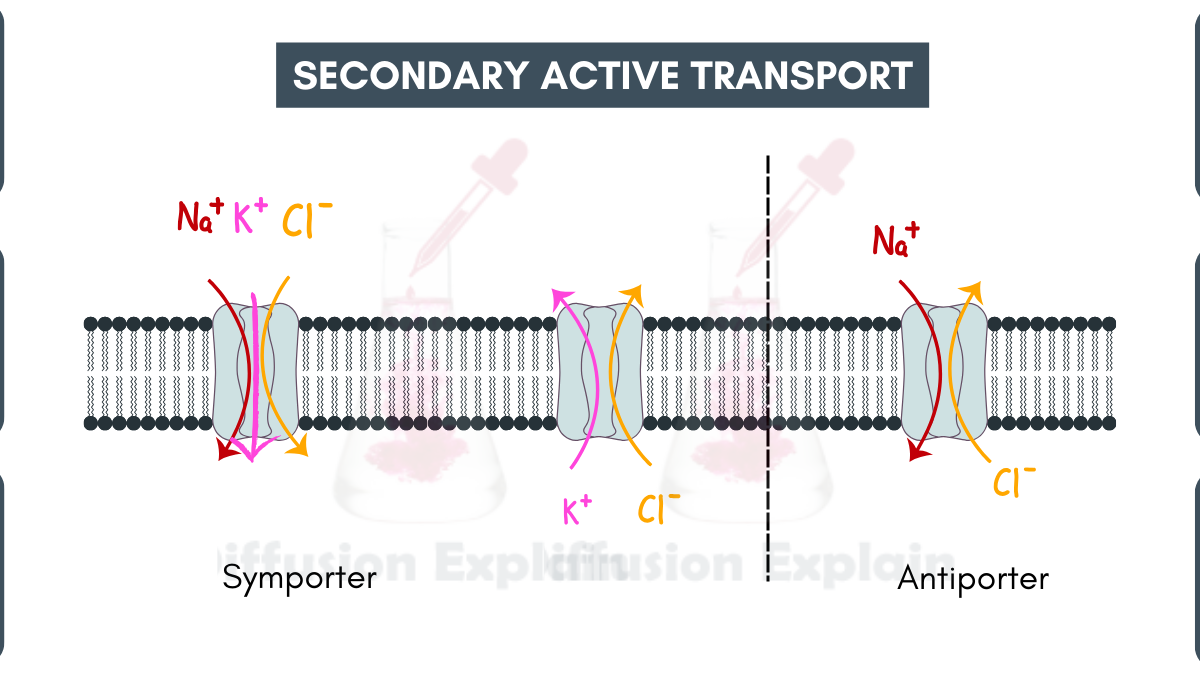
Active transport is a cellular process in which molecules or ions are moved across a biological membrane against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This movement requires the expenditure of cellular energy, typically in form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).