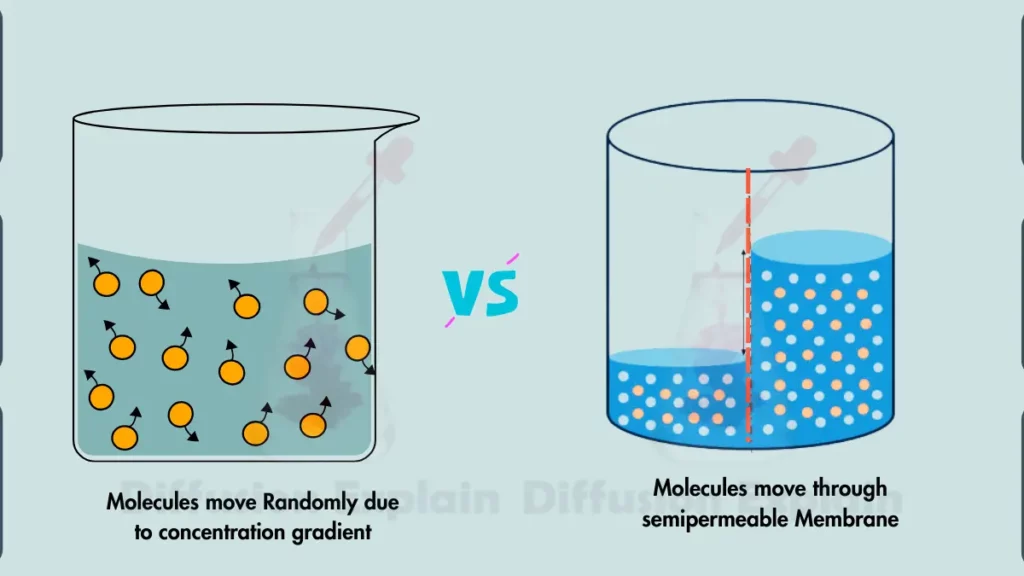
The main difference between simple diffusion and osmosis is the difference of the type of molecule being transported and the driving force behind the movement.
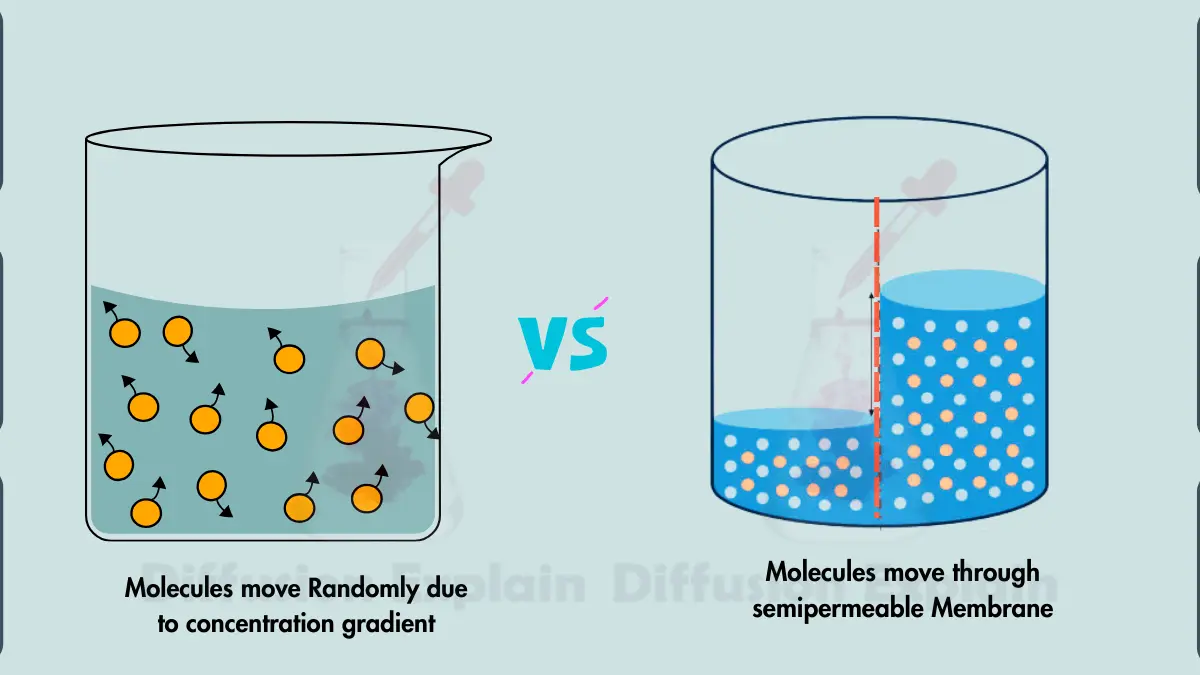
Any molecule with kinetic energy, such as small molecules, gases, and even some ions, can move through diffusion while Osmosis specifically involves the movement of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
Diffusion vs Osmosis
Here are the main differences between Diffusion and Osmosis:
| Osmosis | Diffusion |
|---|---|
| Osmosis primarily transports water molecules across a semipermeable membrane. | Diffusion transports any molecules with kinetic energy, such as small molecules, gases, and ions. |
| Osmosis occurs primarily in liquid mediums. | Diffusion can occur in liquids, gases, or solids. |
| Osmosis requires a semipermeable membrane to separate the solutions. | Diffusion does not require a membrane, although it may be affected by membrane properties. |
| Osmosis is driven by a water potential gradient, which is influenced by the difference in solute concentration. | Diffusion is driven by a concentration gradient, which is the difference in molecule concentration between two areas. |
| Water movement is essential for osmosis to occur. | Water may or may not be involved in diffusion, depending on the diffusing molecule. |
| Osmosis primarily involves the movement of solvent (water) molecules. | Diffusion can involve the movement of both solute and solvent molecules. |
| Osmosis is primarily unidirectional, with water flowing towards areas of lower water potential. | Diffusion can occur in multiple directions, as molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. |
| Osmosis can be stopped or reversed by applying external pressure to the system. | Diffusion is not directly affected by external pressure. |
| Osmosis can occur between solutions of similar or dissimilar concentrations. | Diffusion usually occurs between solutions of similar concentrations, although it may happen across different phases. |
| Osmosis has limited solute movement due to the flow of water across the membrane. | Diffusion allows solute movement along the concentration gradient, promoting equalization of solute concentrations. |
| In osmosis, solvent concentration may or may not equalize between the solutions. | In diffusion, solute concentration tends to equalize between the two areas. |
| Osmosis is strongly dependent on solute potential, which affects the direction and rate of water movement. | Diffusion is not directly dependent on solute potential, pressure potential, or water potential. |
| In osmosis, molecules move from areas of low water potential to areas of high water potential. | In diffusion, molecules move from areas of high energy/concentration to areas of low energy/concentration. |
| Osmosis may be involved in mineral/nutrient uptake, particularly in plants. | Diffusion can indirectly assist in nutrient uptake by transporting molecules across membranes. |