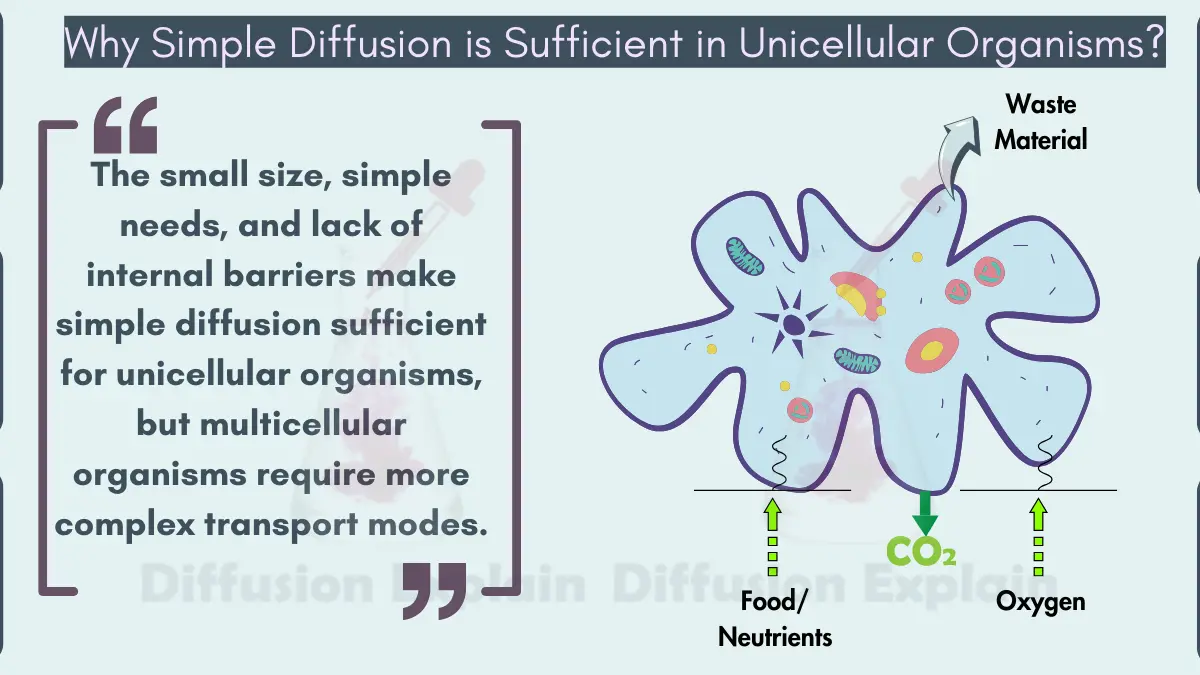
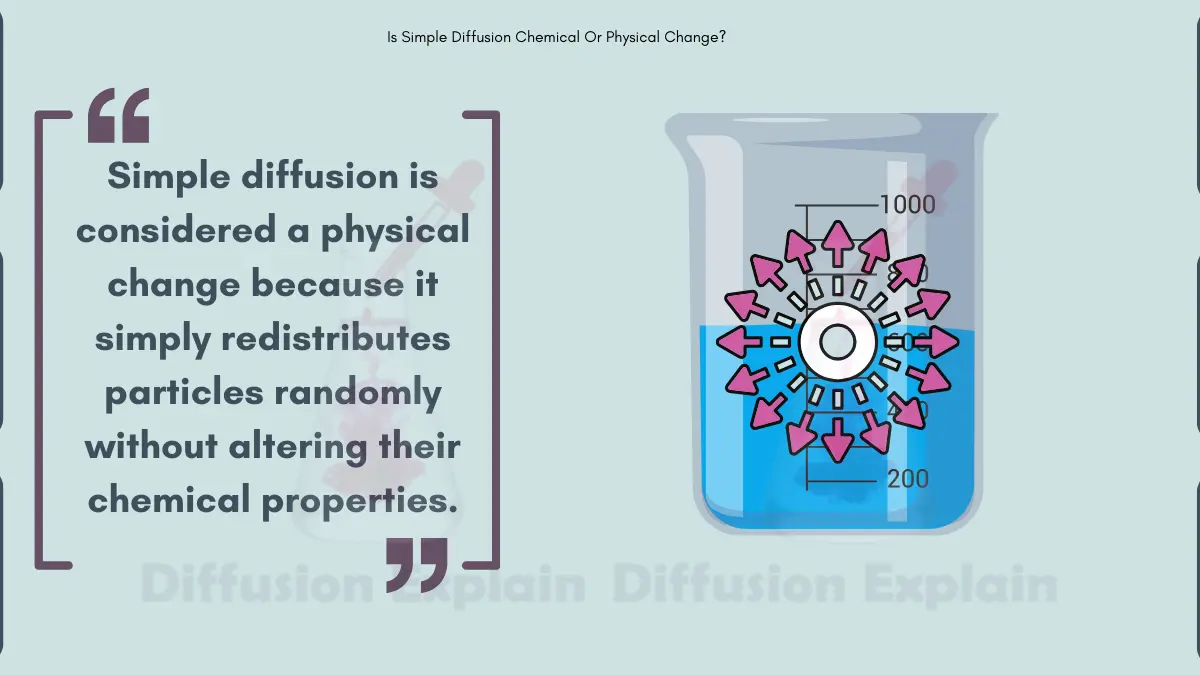
Concentration Gradient-Role in Transport & its Examples
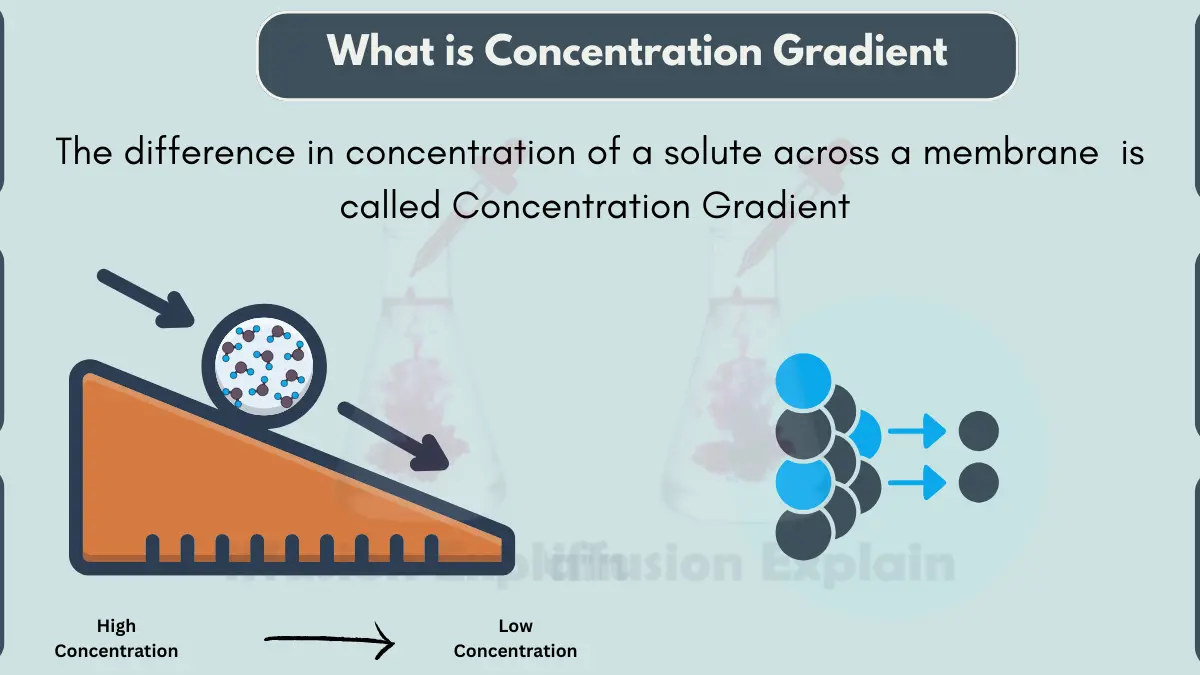
What is Concentration Gradient? A concentration gradient is the difference in the amount or concentration of something between two points or locations. In simple words, it means that there is more of something in one place compared to another place. For example, if you put some sugar in a glass of water and don’t stir … Read more